Proteins are fundamental to life, serving as the building blocks of cells and organs, and are pivotal in nearly every biological process. This comprehensive exploration goes into great detail on what proteins are, their critical importance in nutrition, their multifaceted roles in the human body, the benefits of adequate protein intake, and the potential risks associated with protein consumption. In addition to common sources like high protein foods, this article aims to unravel the complex nature of proteins and their broad impact on health and well-being.
One’s journey into the world of proteins will extend beyond their basic definitions, offering a deeper understanding of their structural complexities, diverse functionalities, and their essential role in both physical and metabolic health. From muscle synthesis to hormonal balance, proteins are integral to maintaining the body’s equilibrium and resilience. Protein is more than just a supplement or a label on a box, it is a complex macronutrient your body needs.
What Does Protein Mean in Nutrition?
In nutrition, protein is much more than a dietary component; it’s a macronutrient composed of amino acids, essential for the body’s structural and functional integrity. Beyond their role as building blocks for muscles and other tissues, proteins are crucial for growth, repair, and maintenance of the body, facilitating numerous physiological processes, including energy supply, hormone regulation, and immune system support.
An understanding of what is protein encompasses its many roles in health, not limited to muscle growth and repair but extending to its vital functions in maintaining life itself. For that reason, protein is an important macronutrient that one must understand when it comes to nutrition and fulfilling a well balanced diet.
Proteins are more than mere nutrients; they are dynamic components of every cell and tissue in the human body. They contribute to the strength and resilience of muscles, the flexibility of joints, and the robustness of the immune system. Their presence in the diet is not just a matter of fulfilling a nutritional requirement; it’s about ensuring the body’s optimal functioning and long-term health.
Why Is It Called a Protein?
The term “protein” originates from the Greek word “proteios,” meaning “primary” or “of the utmost importance,” signifying the protein’s fundamental role in the body’s biological processes. As the primary elements of life, proteins are involved in almost every function within the body. From building cellular structures to facilitating critical chemical reactions, the name ‘protein’ reflects their essential nature and omnipresence in biological systems.
What Is Protein Made Of?
Proteins are composed of long chains of “amino acids,” which are organic compounds made up of carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, and sometimes sulfur. These amino acids are linked by peptide bonds, forming long chains that fold into specific shapes. The sequence and structure of amino acids in a protein dictate its function, enabling proteins to fulfill a vast array of roles within the body.

What Is the Importance of Proteins?
Proteins are indispensable for life. They are essential for building and repairing tissues, including muscles and bones, producing enzymes and hormones, and supporting the immune system. The body relies on proteins for its structural integrity and for the maintenance of all its functions. An adequate supply of protein is vital for health, affecting everything from physical strength to immune response.
What Is the Primary Function of Proteins in the Body?
The primary function of proteins is diverse, encompassing the building and repairing of tissues, especially muscles, and facilitating metabolic reactions. Proteins are also crucial for transporting molecules throughout the body, providing structural integrity to cells and tissues, and regulating bodily functions through hormones and enzymes. The question of “what does protein do for your body” reveals its multifaceted roles in sustaining life and health.
Are Proteins Involved in Muscle Building?
Yes, proteins are fundamentally involved in muscle building. They supply the essential amino acids necessary for muscle protein synthesis, the process of repairing and building muscle tissue. This function is especially critical for athletes, bodybuilders, and anyone engaged in regular physical activity, as it supports muscle recovery and growth.
How Do Proteins Work?
Proteins function through various mechanisms. As enzymes, they catalyze biochemical reactions, essential for life-sustaining processes. Structurally, proteins like collagen provide support and shape to cells and tissues. Proteins also play roles in transporting substances, such as hemoglobin carrying oxygen in the blood, and in regulating body functions via hormones.
What Are Some Examples of Proteins in the Body?
The body contains numerous types of proteins, each with specific roles. Examples of these vital proteins include enzymes, which facilitate and accelerate essential chemical reactions; hemoglobin, which transports oxygen throughout the body; antibodies, which defend against infections; and collagen, which provides structural support to tissues. Each type of protein plays a distinct and critical role in maintaining health and functionality.
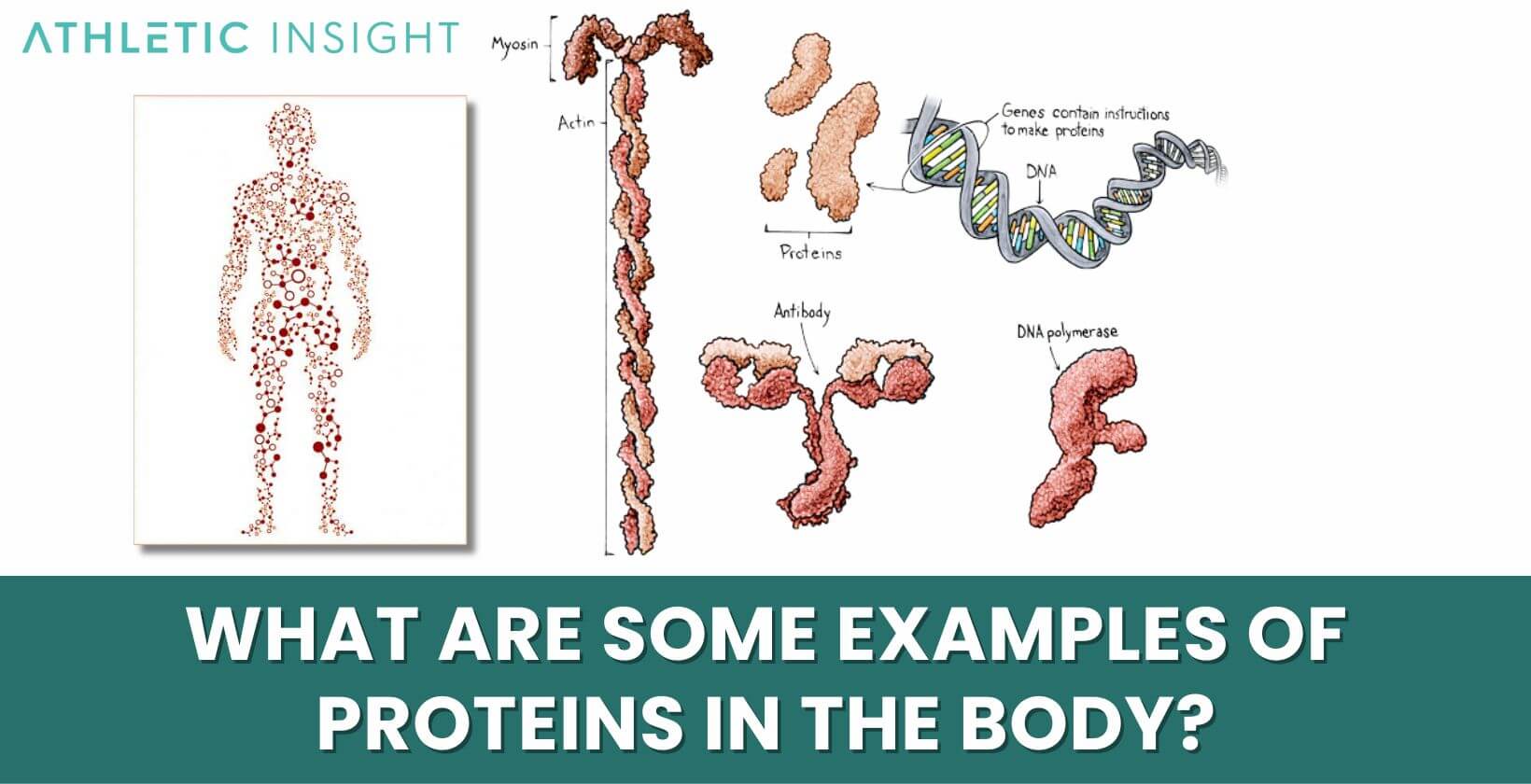
- Enzymes
- Hemoglobin
- Antibodies
- Collagen
1. Enzymes
Enzymes are specialized proteins that act as catalysts in the body, speeding up chemical reactions essential for life. These reactions range from digestion to energy production and cellular repair. These enzymes are vital in managing metabolic processes, ensuring that the body’s complex biochemical systems operate efficiently and effectively.
2. Hemoglobin
Hemoglobin is a protein found in red blood cells, essential for transporting oxygen from the lungs to the body’s tissues and returning carbon dioxide to the lungs for exhalation. Its role is crucial in maintaining the body’s energy levels and overall vitality, showcasing how proteins are integral to the body’s respiratory and circulatory systems.
3. Antibodies
Antibodies are proteins produced by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign invaders, such as viruses and bacteria. Their role is paramount in the body’s defense against illness and infection, highlighting proteins’ critical role in maintaining health and preventing disease.
4. Collagen
Collagen, the most abundant protein in the human body, provides structural support to skin, bones, and connective tissues. The collagen plays a significant role in tissue repair, wound healing, and maintaining skin elasticity and joint mobility, exemplifying proteins’ structural and functional importance.
What Is the Role of Proteins in Diet?
Proteins play a crucial role in one’s diet plan, contributing not only to muscle growth but also to overall health and well-being. They are vital for maintaining lean body mass, supporting metabolic functions, and providing satiety, which helps regulate appetite and food intake. Proteins also contribute to the synthesis of hormones and enzymes, making them indispensable for a balanced and healthy diet.
Do Proteins Help in Weight Loss?
Yes, proteins can be instrumental in weight loss efforts. They provide a sense of fullness, helping to reduce overall calorie intake. Additionally, proteins have a higher thermic effect compared to fats and carbohydrates, meaning they require more energy for digestion, absorption, and metabolism, potentially leading to increased calorie burning. This higher thermic effect, combined with their role in maintaining muscle mass during caloric deficits, makes proteins a valuable macronutrient in weight management strategies.
What Types of Diets Utilize the Use of Proteins?
Various diet types emphasize the importance of proteins for different health goals. For example, the ketogenic diet relies on a high intake of proteins and fats to stimulate ketosis, a metabolic state where the body burns fat for fuel instead of carbohydrates. The Paleo and Atkins diets focus on protein for its perceived role in ancestral nutrition and its capacity to provide prolonged energy and satiety. The Mediterranean diet, known for its balanced approach, includes proteins for their beneficial effects on heart health and overall well-being.
What Are the Sources of Proteins?
Proteins are found in both animal and plant-based foods. Animal-based sources, such as meat, fish, dairy, and eggs, are often complete proteins, containing all essential amino acids. Plant-based sources like beans, lentils, nuts, and seeds are typically incomplete proteins but can form complete proteins when combined appropriately. Understanding the variety of protein sources is crucial for dietary planning, particularly for those with specific dietary preferences or restrictions.

How Do Complete vs Incomplete Proteins Differ?
Complete proteins contain all nine essential amino acids in adequate amounts, necessary for the body’s various functions. In contrast, incomplete proteins lack one or more of these amino acids. This distinction between complete vs incomplete proteins is vital for dietary planning, especially for vegetarians and vegans, who need to combine different plant-based proteins to achieve a complete amino acid profile for optimal health.
What Is the Recommended Protein Intake Every Day?
The recommended daily protein intake is dynamic and individualized, generally suggested at 0.8 grams per kilogram of body weight. However, this can vary based on factors like age, activity level, and overall health. For those engaged in heavy physical activity, such as athletes, the requirement might be higher, ranging from 1.2 to 2.0 grams per kilogram, to support muscle repair and growth.
Elderly individuals might also benefit from increased protein intake to counteract age-related muscle loss. This flexible approach ensures that protein intake is tailored to meet the specific needs and lifestyle of each individual.
What Are the Health Benefits of Proteins?
Proteins offer a multitude of health benefits, crucial for various bodily functions. They are essential for muscle growth and repair, particularly important for athletes and those engaging in regular physical activity. Proteins also play a key role in hormone production and regulation, impacting various bodily functions such as metabolism and mood.
Proteins are also vital for maintaining healthy skin, hair, and nails, contributing to overall physical appearance and health. The immune system also relies heavily on proteins to produce antibodies, which are crucial in fighting off infections and diseases. Lastly, proteins aid in tissue repair and wound healing, showcasing their significance in recovery processes.
What Are the Health Risks of Proteins?
While proteins are essential for health, excessive intake, especially from certain animal sources, can pose health risks. These include potential kidney strain in individuals with pre-existing kidney conditions, as high levels of protein can increase the kidneys’ workload in processing waste products. A diet excessively high in proteins, particularly animal proteins, can also lead to imbalances in nutrient intake and increased consumption of saturated fats and cholesterol, potentially raising the risk of heart disease. It’s therefore crucial to consume proteins in moderation and balance them with other nutrients for a well-rounded diet.
Does Consuming Excess Proteins Damage the Kidney?
For individuals with healthy kidneys, normal protein intake generally does not pose a significant risk. However, excessive protein consumption, particularly over a prolonged period, can place additional strain on the kidneys. This is particularly concerning for those with pre-existing kidney disorders, as their ability to process and eliminate the byproducts of protein metabolism can be compromised.



