A hypertonic solution contains a higher concentration of solutes compared to another solution. When two solutions with unequal solute concentrations exist on either side of a semipermeable membrane, water will move across the membrane from the side with the lower solute concentration (hypotonic) to the side with the higher solute concentration (hypertonic). This movement of water is called osmosis. Understanding hypertonic solutions and how they create osmotic pressure is important in many biological processes and medical treatments.
What is Hypertonic Solution?
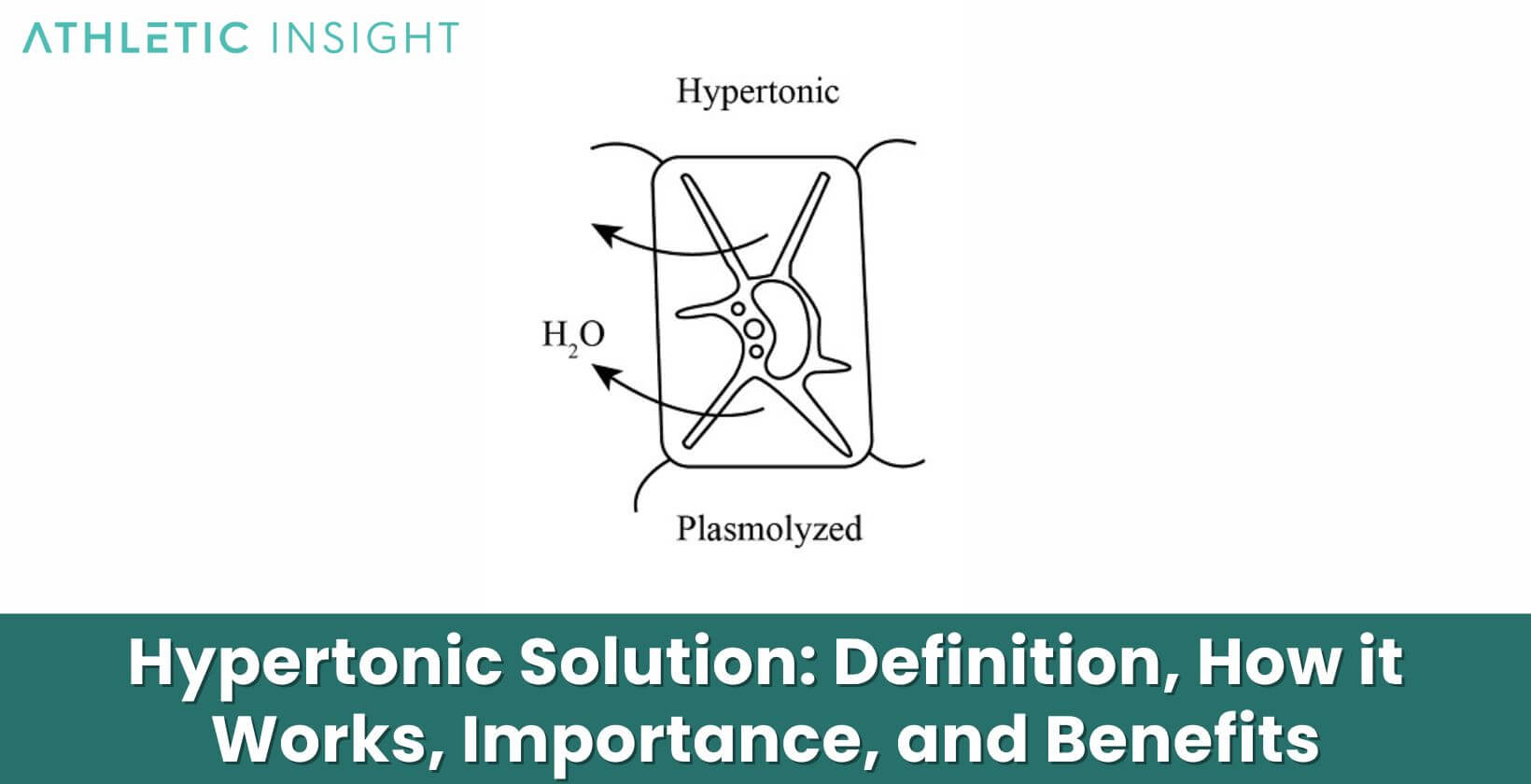
A hypertonic solution refers to a solution that has a higher solute concentration than another solution. The word “hypertonic” comes from the Greek words “hyper”, meaning over or above, and “tonikos”, meaning tension or tone. Thus, a hypertonic solution has a greater tone or tension than another solution due to its higher solute content.
For example, seawater is hypertonic compared to the cytoplasm inside most living cells. The seawater contains a higher concentration of dissolved salts and other molecules than the fluid inside the cells. If a cell were placed in seawater, water would leave the cell and enter the seawater in an attempt to equalize the solute concentrations. This loss of water would cause the cell to shrivel.
How does Hypertonic Solution work?
A hypertonic solution works by creating an osmotic pressure gradient across a semipermeable membrane. A semipermeable membrane allows smaller solvent molecules to pass through but blocks larger solute molecules. When a hypertonic solution exists on one side of a semipermeable membrane and a hypotonic solution with a lower solute concentration exists on the other side, water will diffuse across the membrane from the hypotonic side to the hypertonic side.
This net movement of water molecules is called osmosis. It occurs until equilibrium is reached and the solutions are isotonic, meaning they have equal solute concentrations. The osmotic pressure generated by the hypertonic solution pulls water out of cells and tissues on the hypotonic side, causing them to shrink as they lose water to the hypertonic solution.
What is the function of Hypertonic Solution in the body?
In the human body, hypertonic solutions can draw excess water out of cells and tissues. For example, the renal medulla in the kidneys uses hypertonic interstitial fluid to concentrate urine by pulling water out of the collecting ducts. Hypertonic saline solutions can also be used medically to draw fluid out of edematous tissues in conditions like congestive heart failure.
Hypertonic solutions in the digestive tract pull water into the intestines via osmosis to promote regularity and treat constipation. The high solute concentration in hypertonic sports drinks like Gatorade helps replenish fluids and electrolytes lost through sweating during exercise.
What is the importance of the Hypertonic Solution?
Hypertonic solutions are important for regulating fluid and electrolyte balance in the body. Osmosis driven by hypertonic fluids controls water movement between bodily compartments and is essential for proper hydration at the cellular level.
In medicine, hypertonic solutions have a variety of therapeutic uses including reducing edema, aiding in digestive regularity, promoting urine concentration in kidney function, and replacing electrolyte losses. The high solute content of hypertonic sports drinks makes them better at rehydrating athletes than plain water.
How important is Hypertonic Solution in Sports Nutrition?
Hypertonic solutions are very important in sports nutrition to optimize athletic hydration and performance. The high solute concentration found in popular sports drinks like Gatorade pulls fluid into the digestive tract faster than plain water. This promotes rapid absorption and replenishment of fluids lost through sweat.
The sugars and electrolytes in these hypertonic drinks also provide energy and help maintain muscle and nerve function during intense exercise. Research shows hypertonic sports beverages hydrate better and can improve endurance in athletes compared to hypotonic options.
Does Hypertonic Solution Enhance Hydration?
Yes, hypertonic solutions do enhance hydration compared to plain water. The osmotic pull created by their higher solute concentration accelerates fluid absorption across the intestinal lining. Hypertonic sports drinks with sugars and electrolytes also promote better hydration by replenishing not just water but also energy stores and electrolytes lost through sweating.
Studies show hypertonic drinks provide superior hydration and performance benefits compared to isotonic and hypotonic beverages in athletes engaging in prolonged, intense exercise in hot conditions.
What are examples of a Hypertonic Solution?
Some examples of hypertonic solutions include:
- Seawater
- The interstitial fluid in the renal medulla of the kidneys
- Oral rehydration salts used to treat diarrhea
- Hypertonic saline injections used clinically to draw fluid out of edematous tissues
- Commercial sports drinks like Gatorade, Powerade, and Pedialyte
- Cola soft drinks
Are drinks like Gatorade and Powerade Hypertonic Solution?
Yes, typical sports drinks like Gatorade and Powerade are hypertonic solutions. They contain high concentrations of sugars, salts, and electrolytes compared to the body’s normal fluid compartments. The extra solutes make these drinks hypertonic, creating an osmotic pressure that accelerates fluid absorption from the digestive tract into the bloodstream.
This helps rapidly replace sweat losses and improves hydration efficiency compared to drinking plain water. The carbohydrates and electrolytes in the drinks also provide energy and aid muscle function.
Are IV fluids Hypertonic Solutions?
Some IV fluids are hypertonic solutions, while others are isotonic or hypotonic. Hypertonic saline is sometimes given intravenously to draw excess fluid out of edematous tissues or elevate low blood sodium levels. However, normal IV fluids used for hydration like 0.9% saline and lactated Ringer’s solution are isotonic and formulated to match the body’s natural osmolarity.
Hypotonic IV fluids may be given to replenish pure water losses without affecting electrolyte balance. The tonicity of IV fluids given depends on the specific clinical circumstances.
What are the Benefits of Hypertonic Solution?
Hypertonic solutions offer many benefits for the body. They facilitate swift water absorption into the circulatory system by crafting an osmotic gradient. This feature ensures that individuals, especially athletes, can rehydrate and replenish lost electrolytes efficiently during strenuous exercise.
Beyond hydration, these solutions are a boon for energy provision, thanks to their carbohydrate content. In medical contexts, they serve as a remedy for edema, drawing out surplus fluids from swollen tissues.
Also, those facing digestive irregularities can find solace in these solutions as they promote bowel regularity by channeling water into the intestines. Not to be overlooked, they also play a pivotal role in the renal system, concentrating urine in the kidneys through osmotic pressure, ensuring optimum kidney function.
- Rapidly absorbs water into the circulatory system by creating an osmotic gradient
- Rehydrates and replenishes electrolytes efficiently, especially during exercise
- Provides energy through carbohydrate content
- Reduces edema by pulling excess fluid from tissues
- Promotes bowel regularity by drawing water into the intestines
- Concentrates urine in the kidneys via osmotic pressure
What are the Limitations or Disadvantages of Hypertonic Solution?
- Can cause cellular dehydration and shrinkage if overly hypertonic
- Excess electrolytes may cause imbalances in people with kidney dysfunction
- Oral rehydration solutions may cause osmotic diarrhea if improperly formulated
- Repeated IV infusion of hypertonic saline can lead to hypernatremia and hyperchloremia
- May irritate veins with intravenous administration
Despite their benefits, hypertonic solutions are not without drawbacks. One significant concern is their potential to induce cellular dehydration, leading to cell shrinkage if the solution is excessively hypertonic. Individuals, especially those with kidney malfunctions, face the risk of electrolyte imbalances due to the high salt content. When ingested, if hypertonic oral rehydration solutions aren’t precisely formulated, they can usher in osmotic diarrhea, causing discomfort.
On the medical front, continuous intravenous infusion of hypertonic saline might result in conditions like hypernatremia and hyperchloremia, elevated levels of sodium and chloride in the blood respectively. Lastly, direct intravenous administration can irritate veins, making it a less favored option for some patients.
What is the difference between Hypertonic, Hypotonic, and Isotonic Solutions?
The key difference between hypertonic, hypotonic, and isotonic solutions is the concentration of solutes they contain relative to a reference solution:
- Hypertonic: Higher solute concentration than the reference solution
- Hypotonic: In a Hypotonic Solution, there is lower solute concentration than the reference solution
- Isotonic: With an Isotonic Solution, there is equal solute concentration to the reference solution
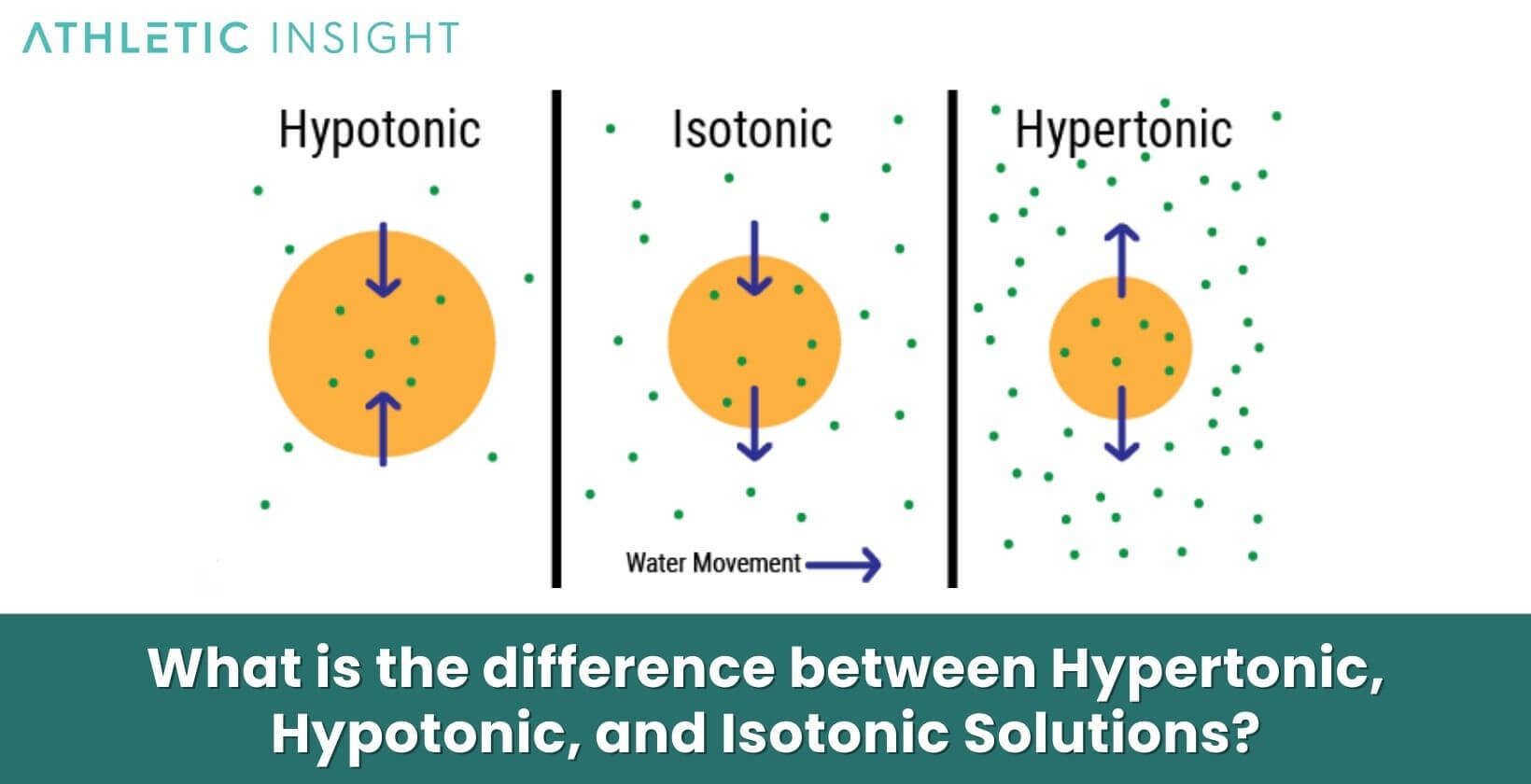
In the body, the reference solution is usually extracellular fluid or blood plasma. Hypertonic fluids like the renal medulla pull water from cells and hypotonic fluids like distilled water flow into cells. Isotonic solutions like 0.9% saline do not alter cell volume.