Isotonic solutions play an essential role in biology and medicine, ensuring that cell environments maintain balance and function properly. When you hear the term “isotonic solution”, think of equilibrium. It’s about creating a space where cells can thrive without too much or too little water. This article will delve into what an isotonic solution is, how it operates, some common examples, and its many benefits.
What is Isotonic Solution?
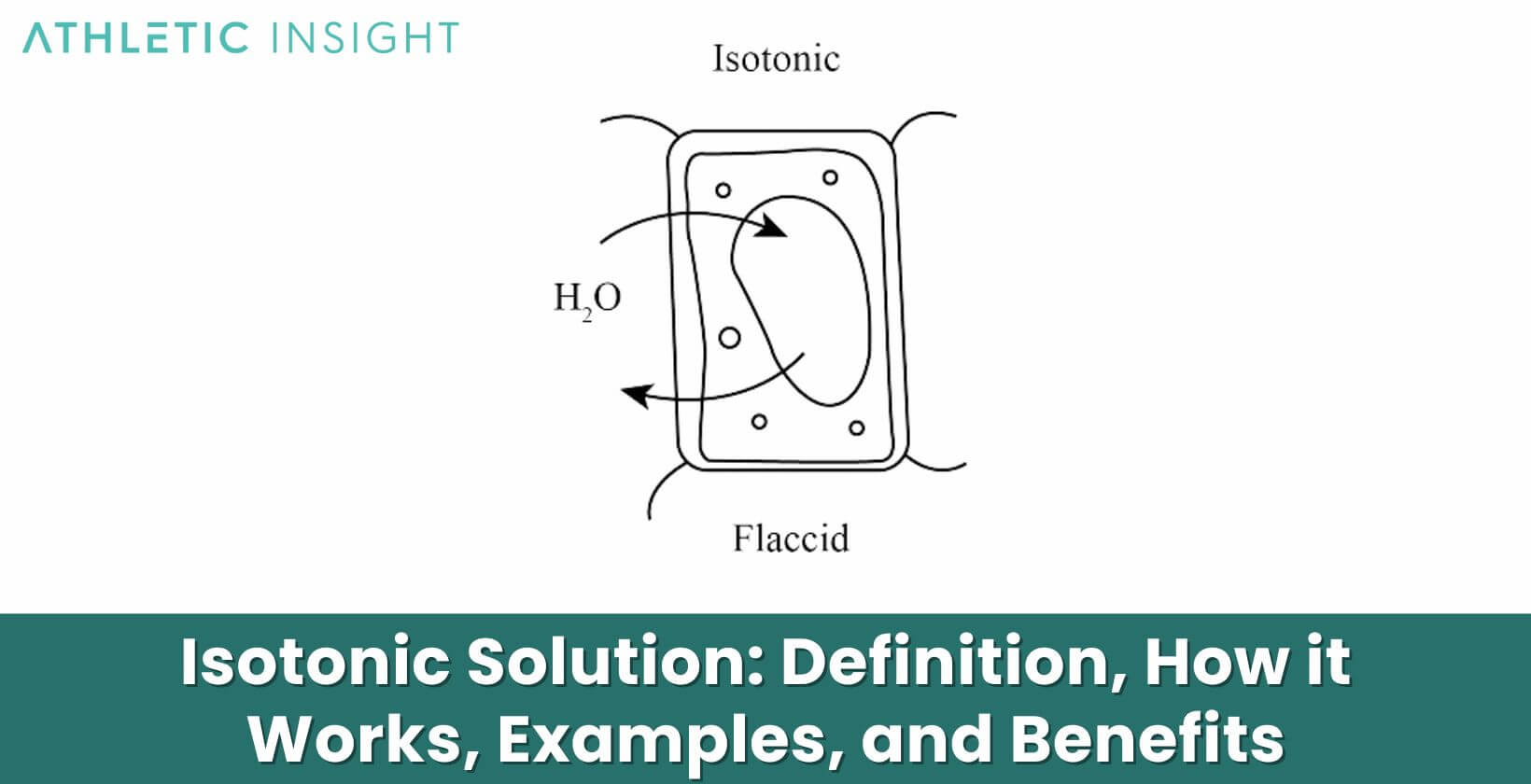
At its core, an isotonic solution is one where the concentration of solutes outside the cell is equal to the concentration inside the cell. This balance ensures that the amount of water entering and exiting the cell is the same, resulting in a stable cell environment. It’s like a seesaw in perfect balance, where neither side is up nor down.
Such solutions are pivotal in medical settings, especially when fluids need to be administered to patients. By understanding the characteristics of isotonic solutions, healthcare professionals can ensure that they’re providing the most effective care to their patients, especially in circumstances where the body’s fluid balance might be disrupted, such as during surgery or severe dehydration.
How does Isotonic Solution work?
An isotonic solution functions by maintaining an equilibrium. When cells are in an isotonic environment, the flow of water into and out of the cell is constant and equal. This steady state means cells are not at risk of swelling from too much water or shrinking due to water loss. Imagine a door that allows as many people to enter as those leaving, maintaining a balanced number inside.
For the human body, isotonic solutions are especially valuable. When there’s a need to replace lost fluids, such as after surgery or during dehydration, these solutions help ensure that cells don’t become overwhelmed with too much or too little water. This balance supports cellular functions and contributes to overall health.
What is the importance of the Isotonic Solution?
Isotonic solutions bear significant importance in both medical and biological contexts. Their ability to maintain cellular equilibrium helps in sustaining life and ensuring cellular activities proceed without interruption. Any imbalance can lead to detrimental effects, potentially causing cells to burst or shrivel. Hence, maintaining isotonicity is crucial.
In the realm of sports nutrition, isotonic solutions are highly regarded. Athletes often lose fluids and electrolytes during intensive physical activities. Consuming isotonic drinks helps replenish these vital components, ensuring muscles continue to function optimally and reducing the risk of cramps. It’s akin to giving a car the right type of fuel it needs to run smoothly.
What does Isotonic Solution do?
Isotonic solutions serve multiple functions, particularly in the medical world. Firstly, they aid in maintaining the volume of the cell’s cytoplasm by ensuring a balance of water entering and leaving the cell. This balance is essential for maintaining the shape, size, and overall health of the cell. Without this balance, cells can become damaged or even die, leading to potential complications in bodily functions.
Moreover, isotonic solutions are frequently employed in healthcare settings. They’re used as intravenous fluids to rehydrate patients, support fluid loss during surgery, and treat dehydration. Their balanced nature ensures that they don’t disrupt the body’s internal balance, making them an excellent choice for numerous medical applications.
How does Isotonic Solution improve Sports Performance?
Isotonic solutions offer athletes a way to optimize their performance. Intense physical activity can cause significant loss of fluids and electrolytes through sweat. This loss can result in decreased performance, fatigue, and muscle cramps. Isotonic drinks, often packed with essential electrolytes, help replenish the body’s lost fluids, ensuring muscles receive the necessary nutrients for contraction and relaxation.
Additionally, these solutions provide a quick source of energy. The carbohydrates found in some isotonic drinks give athletes the much-needed boost during prolonged physical exertions. Thus, by staying hydrated with isotonic solutions, athletes can maintain their energy levels, focus, and endurance, allowing for peak performance.
How can isotonic solutions optimize hydration during Sports Performance?
Hydration is a linchpin for athletic success and overall sports performance. An isotonic solution, being equal in concentration to body fluids, provides rapid hydration without causing an imbalance. It ensures that while water is being replaced, essential salts and minerals lost through sweat are replenished concurrently. This twofold action keeps athletes’ bodies in balance, preventing issues like dehydration or electrolyte imbalances that can impair performance.
Isotonic solutions are also absorbed quickly by the digestive system. This means athletes don’t have to wait long to feel the effects. The rapid absorption ensures that dehydration is curtailed swiftly, allowing athletes to recover and return to their activities with minimal downtime.
Does Isotonic Solution Affect metabolism?
Yes, isotonic solutions can influence metabolism. When athletes engage in intensive workouts, their metabolic rates skyrocket, burning energy rapidly. Here, isotonic solutions come into play. Packed with sugars like glucose, they provide a quick energy source, aiding metabolic processes. These solutions support cells in generating ATP, the primary energy currency in the body, ensuring continuous cellular functions and energy availability.
So, maintaining fluid balance is integral for metabolic reactions. Proper hydration ensures that enzymatic reactions, crucial for energy production and nutrient utilization, occur efficiently. Without balanced hydration, metabolic processes could slow down, reducing energy production and negatively impacting performance.
Does the Isotonic Solution affect an athlete’s mental focus?
Yes, isotonic solutions can impact an athlete’s mental focus. Dehydration, even if minor, can impair cognitive functions. It may lead to issues like reduced concentration, increased perception of effort, and even mood disturbances. When an athlete is well-hydrated using an isotonic solution, their brain remains optimally functional.
By ensuring the right balance of fluids and electrolytes in the body, isotonic solutions safeguard against the negative cognitive effects of dehydration. As a result, athletes can remain alert, make quicker decisions, and maintain their strategic edge during competitions and training.
What are the examples of Isotonic Solutions?
Several solutions fall under the category of isotonic, widely used in clinical settings and sports nutrition. These solutions have a solute concentration that mirrors the body’s cells, ensuring balanced hydration without causing cellular swelling or shrinking. Some well-known examples include:
- Ringer’s Solution
- Lactated Ringer’s Solution
- Normal Saline (0.9% Sodium Chloride)
- 5% Dextrose in Water (D5 W)
1. Ringer’s Solution
Ringer’s Solution is a type of isotonic fluid containing sodium, potassium, and calcium in concentrations similar to the body’s plasma. It’s primarily used for fluid replacement in clinical settings to restore electrolyte balance. When a person loses fluids, be it from surgery, trauma, or illness, Ringer’s solution helps in replenishing lost elements and restoring fluid balance.
One of the chief advantages of Ringer’s Solution is its similarity to the body’s natural fluid composition. This likeness ensures that when the solution is introduced into the bloodstream, it doesn’t cause any sudden changes in cellular sizes. Instead, it promotes optimal cellular function and overall physiological balance.
2. Lactated Ringer’s Solution
Lactated Ringer’s Solution is akin to the Ringer’s Solution but includes an additional component: lactate. This compound acts as a buffer, converting to bicarbonate in the body and helping to adjust the pH levels, especially during acidosis situations.
This solution is often chosen in clinical situations where patients might be dealing with acid-base imbalances. For instance, in cases of significant blood loss or burn injuries, Lactated Ringer’s can not only replenish lost fluids but also restore the body’s pH to its optimal range, ensuring vital organs function efficiently.
3. Normal Saline (0.9% Sodium Chloride)
Normal Saline, made up of 0.9% Sodium Chloride, stands as one of the most frequently used isotonic solutions. Its primary advantage is its simplicity. Comprising just salt and water, it mirrors the salt concentration of human cells, making it an ideal choice for fluid replacement.
In the medical world, Normal Saline finds use in numerous applications. These include fluid resuscitation, dilution of medications for intravenous administration, and even as a flushing agent for intravascular catheters. Its capability to balance fluid without causing cellular disruptions makes it indispensable in hospitals and clinics.
4. 5% Dextrose in Water (D5 W)
5% Dextrose in Water, commonly known as D5 W, is an isotonic solution initially. It contains 5% dextrose dissolved in water. Once introduced into the body, cells promptly absorb the dextrose, leaving behind pure water—a hypotonic solution.
This unique characteristic of D5 W means it’s utilized in situations where both energy (from glucose) and water need replenishing. It’s especially valuable in treating dehydration and providing calories to individuals who might not be ingesting food. However, care must be taken with its administration, as the rapid dextrose absorption can lead to cellular swelling if not monitored.
What are the benefits of the Isotonic Solution?
Isotonic solutions offer several benefits that make them indispensable in medical and sports scenarios. For one, they closely mirror the body’s own fluid composition, reducing the risk of rapid cellular changes. They also aid in maintaining physiological stability by restoring lost fluids and electrolytes. This makes them ideal for situations such as dehydration, fluid loss after surgery, or strenuous exercise.
Another significant advantage is their ability to serve as a diluent for intravenous medication. Because of their balanced nature, they allow for the even distribution of drugs within the bloodstream, enhancing therapeutic efficacy. Thus, isotonic solutions are not just for rehydration; they contribute to varied medical applications.
What are the limitations of the Isotonic Solution?
Despite their widespread use, isotonic solutions aren’t without limitations. Primarily, they can’t correct severe imbalances in blood pH levels or specialized electrolyte deficits, as they only offer a limited range of ions. They are also not ideal for providing high levels of nutrition or calories.
Moreover, indiscriminate use can lead to issues like fluid overload, especially in patients with compromised heart or kidney function. Careful monitoring is essential to ensure that the solution suits the specific needs of the individual, lest it contributes to further complications.
Is Isotonic Solution the best for Active Dehydration?
While isotonic solutions are good for treating mild to moderate dehydration, they are not universally the “best” for all types of dehydration. Some conditions may require hypotonic or hypertonic solutions, depending on the specific electrolyte imbalances and clinical symptoms involved.
For instance, isotonic solutions are often ideal for dehydration caused by sweating from exercise or heat but may not be suited for dehydration due to severe diarrhea or vomiting, which can result in specific electrolyte imbalances that isotonic solutions alone may not correct.
Are IV Fluids Isotonic Solution?
Not all intravenous (IV) fluids are isotonic. While some of the most commonly used IV fluids like Normal Saline and Lactated Ringer’s are isotonic, there are also hypertonic and hypotonic IV solutions. Each type serves specific medical needs.
Isotonic IV fluids are often used for rehydration and for the dilution of intravenous drugs, as they are balanced and cause minimal cellular disruption. On the other hand, hypertonic solutions are utilized for conditions like hyponatremia, and hypotonic solutions are used in cases of hypernatremia.
What is the difference between Isotonic, Hypotonic, and Hypertonic Solutions?
Understanding the differences between isotonic, hypotonic, and hypertonic solutions is pivotal in the realms of biology and medicine. These terms mainly describe the concentration of solutes in a solution as compared to another solution, often the body’s fluids.
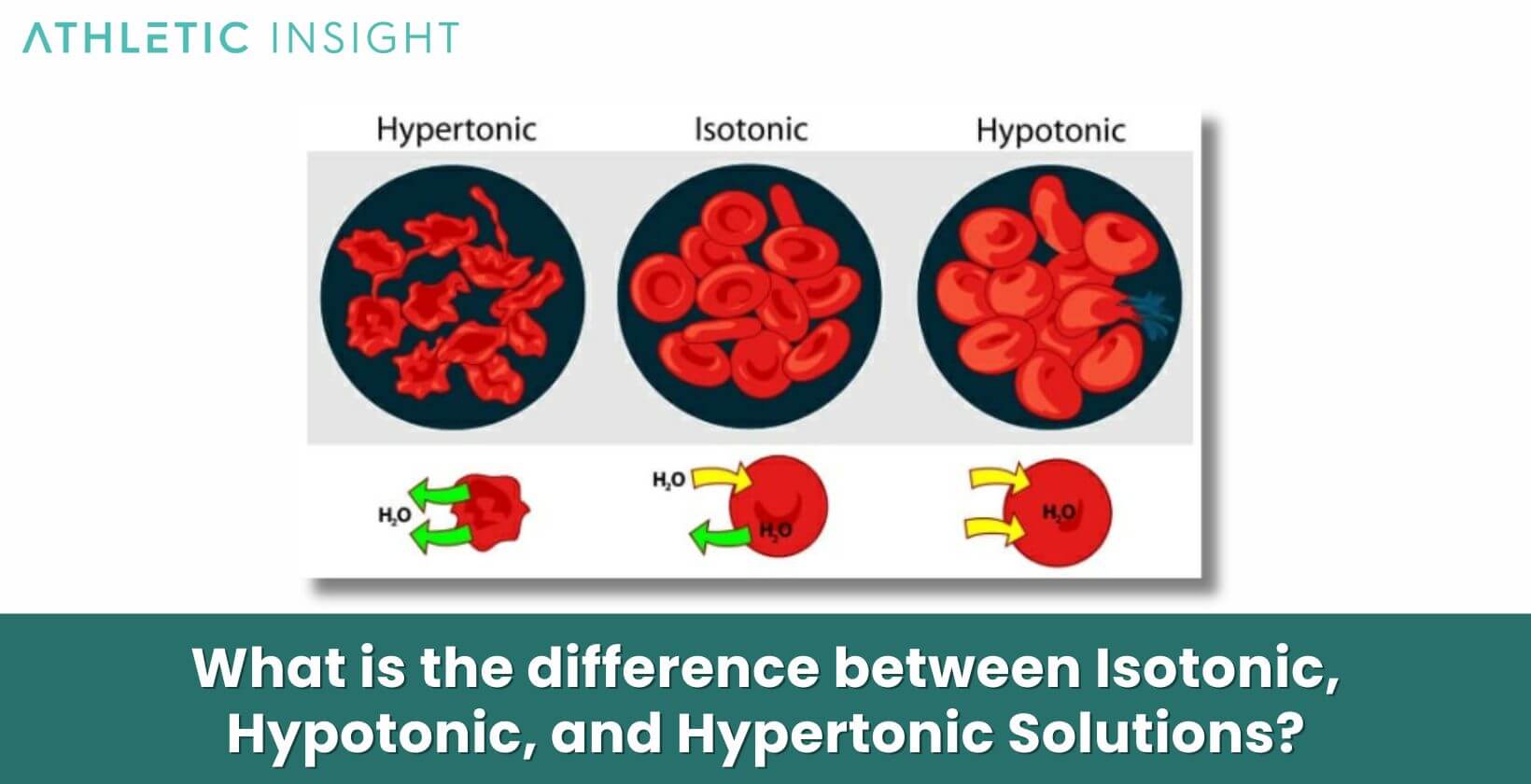
- Isotonic Solutions: Isotonic Solutions have the same concentration of solutes as the body’s cells. This means that when cells are immersed in an isotonic solution, there’s no net movement of water into or out of the cells. Consequently, the cell remains stable, neither shrinking nor swelling. Normal Saline, which is 0.9% sodium chloride, is a typical example. These solutions are often used for fluid resuscitation, as they don’t disrupt the cells’ water balance.
- Hypotonic Solutions: The Hypotonic Solutions contain a lower concentration of solutes compared to the inside of the cells. When cells encounter a hypotonic environment, water moves into the cells, causing them to swell. This can potentially lead to cell rupture or lysis if the influx is excessive. Distilled water is an extreme example of a hypotonic solution.
- Hypertonic Solutions: Hypertonic Solutions possess a higher concentration of solutes than the body’s cells. As a result, when cells are exposed to a Hypertonic Solution, water leaves the cells, leading to cell shrinkage or crenation. These solutions can be useful in cases where it’s essential to decrease cellular swelling, such as cerebral edema. An example is 3% sodium chloride.