N-Acetylcysteine, known as NAC, plays a crucial role in maintaining and supporting human health. It’s renowned for its powerful antioxidant capabilities and is available as both a prescription medication and a dietary supplement. Understanding the appropriate NAC 600 mg dosage, its many health benefits, and potential side effects is vital for anyone considering this supplement. In-depth knowledge of NAC, including the best NAC supplement and its various forms, can guide users to maximize its advantages while minimizing any adverse effects.
What is N-Acetylcysteine (NAC)?
N-Acetylcysteine (NAC) is a modified form of the sulfur-containing amino acid cysteine. It’s primarily used in a medical context to treat acetaminophen overdose by preventing liver damage, and as a mucolytic agent, it breaks down mucus in individuals with chronic respiratory diseases. Its development as a supplement arises from its ability to replenish intracellular levels of the body’s primary antioxidant, glutathione. Consequently, NAC has become a cornerstone in the management of various conditions due to its detoxification and anti-inflammatory capabilities.
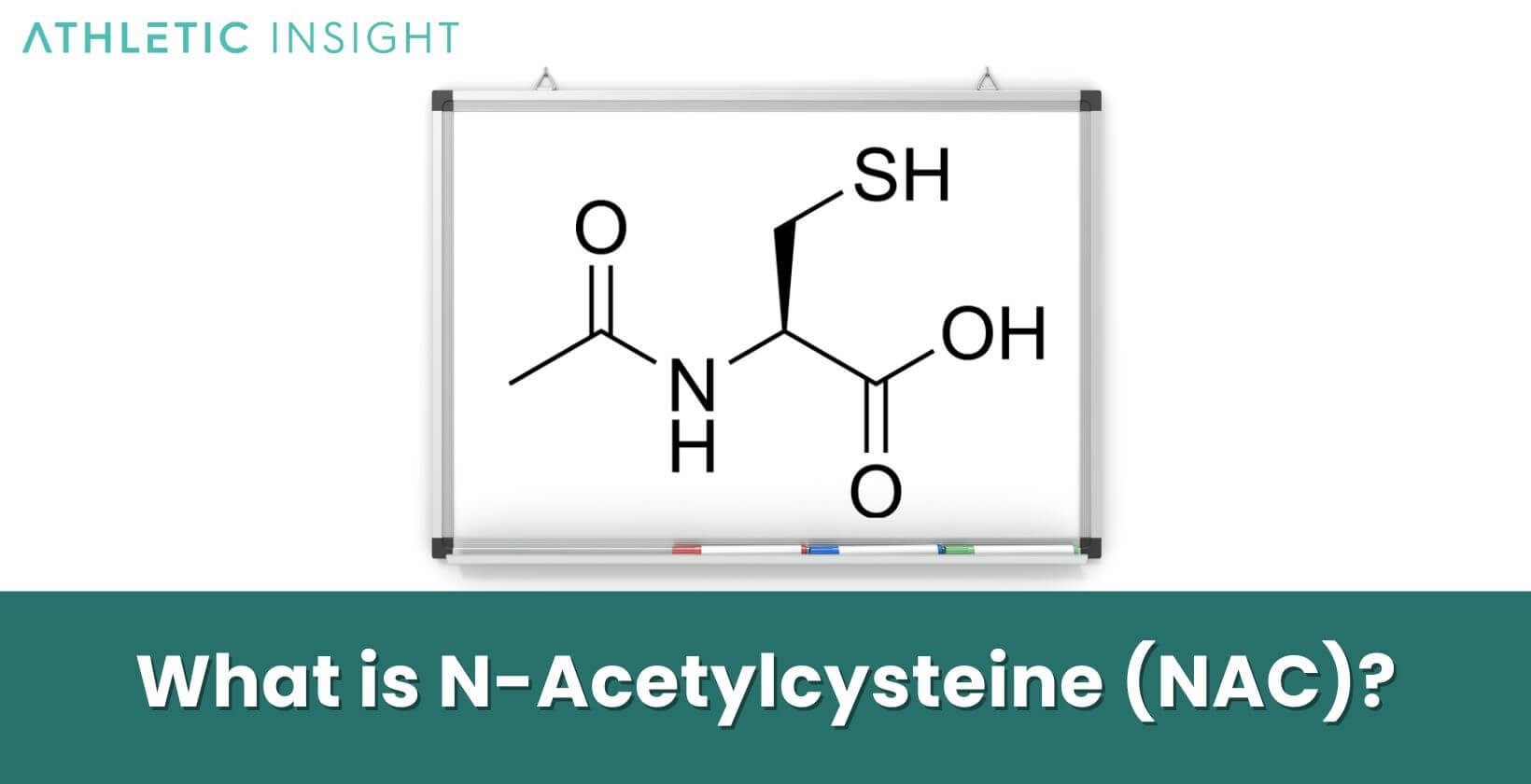
Regarding supplements, NAC is sought after for its antioxidant properties. It scavenges free radicals and serves as a precursor to glutathione, promoting detoxification and bolstering the immune system. Beyond its original purpose, the scope of NAC’s utility has expanded, including its use in psychiatric conditions as it modulates glutamate levels and improves antioxidant defenses within the brain. This dual action on neurotransmitter regulation and oxidative balance makes NAC a unique player in the realm of dietary supplements.
Who Should Take NAC?
Yes, certain individuals should consider taking NAC as a supplement. Those who benefit most are people dealing with chronic respiratory conditions, individuals looking to enhance their body’s antioxidant capacity, and patients with specific psychiatric disorders where oxidative stress is a contributing factor. NAC’s utility in these scenarios is well documented. However, it’s essential for anyone with a pre-existing medical condition or who is pregnant to consult with a healthcare professional before starting NAC to ensure it doesn’t interfere with other medications or conditions.
Moreover, athletes and individuals exposed to high levels of pollutants may also find NAC beneficial due to its ability to support the body’s natural defense systems against oxidative stress and inflammation. As with any supplement, it’s important to tailor the use of NAC to one’s individual health profile and objectives, always considering professional medical advice as a primary decision-making factor.
Is NAC Safe?
Yes, NAC is generally safe when taken as directed. The well-established dosing guidelines provide a framework for the safe consumption of NAC, whether it be for chronic bronchitis, acetaminophen toxicity, or as a dietary supplement. Reported side effects are typically mild and may include gastrointestinal discomfort such as nausea and diarrhea, particularly at higher dosages.
While safe for most individuals, there are specific instances where NAC could pose risks, such as potential interactions with nitroglycerin and the possibility of causing bronchospasm in people with asthma. Therefore, it’s crucial to take NAC under medical supervision, especially in a clinical setting or when using it to manage health conditions. Discussing with a healthcare provider ensures proper monitoring and adjustment of dosages as necessary.
What are the Medical Benefits of N-Acetylcysteine?
N-Acetylcysteine offers a spectrum of medical benefits, substantiated by its role in critical physiological processes. Its primary medical benefit lies in its ability to support the synthesis of glutathione, thereby enhancing the body’s antioxidant defense system. This has implications for a variety of diseases where oxidative stress is a factor, including chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), heart disease, and infertility. Additionally, NAC’s mucolytic action makes it effective in treating respiratory conditions by thinning mucus, easing expectoration, and improving breathing.

Another vital benefit of NAC is its neuroprotective properties, which have been harnessed in the management of psychiatric disorders such as bipolar disorder, depression, and schizophrenia. By modulating neurotransmitters and protecting against oxidative damage, NAC can help to stabilize mood and cognitive function. Its benefits also extend to the prevention of chronic diseases, reduction in inflammation, and potential detoxifying effects in cases of poisoning by heavy metals and other toxins. The broad-reaching benefits of NAC make it a valuable and versatile supplement for various medical applications.
- Supports glutathione synthesis (enhances antioxidant defense system)
- Decreases oxidative stress (COPD, heart disease, infertility)
- Treats respiratory conditions (COVID, mucus, breathing)
- Stabilizes mood and cognitive functions
- Prevention of chronic diseases
- Reduction in Inflammation
- Detoxification of heavy metals and toxins
How Does N-Acetylcysteine Work in The Body?
N-Acetylcysteine exerts its beneficial effects through several mechanisms once ingested. Primarily, it acts as a precursor to glutathione, the body’s most abundant antioxidant. This elevation in glutathione levels helps counteract oxidative stress and protect cells from damage. NAC also influences the levels of cysteine directly, a critical amino acid for protein synthesis and cellular health. Moreover, NAC has a direct impact on the respiratory system by breaking disulfide bonds in mucus, making it less viscous and easier to expel, which is particularly beneficial for individuals with chronic bronchitis or cystic fibrosis.
In addition to these mechanisms, NAC modulates the function of neurotransmitters in the brain. This regulation can have therapeutic effects on mental health conditions, as it impacts both glutamate and dopamine pathways, which are often disrupted in psychiatric disorders. NAC’s ability to regulate these neurotransmitters, combined with its antioxidant effect, offers a two-pronged approach to neuroprotection and the treatment of mental health conditions.
Are There Any Side Effects Associated with NAC?
While NAC is well-tolerated by most people, it can have side effects, particularly when taken in high doses. Common side effects include gastrointestinal issues like nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Some individuals might also experience headaches, dizziness, or allergic reactions, although these are less common. When used as a mucolytic agent through inhalation, NAC may cause bronchospasm, and thus, individuals with asthma should use it cautiously.
As with any supplement or medication, the risk of side effects can be minimized by adhering to the recommended dosages and consulting a healthcare provider before use, especially for individuals with pre-existing conditions or those taking other medications. Monitoring by a healthcare professional is advised to ensure safe use and to manage any adverse effects promptly.
What is the Dosage Recommendation for N-Acetylcysteine?
The recommended dosage for N-Acetylcysteine varies depending on the intended use. For general antioxidant support, dosages typically range from 600 to 1,200 mg per day. In clinical settings, for acetaminophen overdose, higher doses are administered under medical supervision. When it comes to chronic respiratory conditions, a common dosage is 600 mg taken two to three times daily, but this can vary based on the individual’s health status and the severity of the condition.
It’s important to note that while the 600 mg dosage is commonly found in over-the-counter supplements, specific dosing should always be tailored to an individual’s needs and confirmed with a healthcare provider to ensure safety and efficacy. Long-term use or higher doses should be monitored by a medical professional to avoid potential side effects and to ensure that the supplement does not interfere with other medications or health conditions.
How does N-Acetylcysteine compare to Other Treatments or Supplements for Certain Conditions?
N-Acetylcysteine stands out in comparison to other treatments or supplements, particularly due to its multifaceted role and its ability to influence glutathione levels. For conditions like chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) or acetaminophen overdose, NAC is often the treatment of choice because of its specific mucolytic and hepatoprotective properties. In the realm of mental health, NAC is gaining attention for its potential to manage symptoms of depression, bipolar disorder, and schizophrenia, offering an alternative or adjunct to traditional pharmaceuticals that may come with a heavier burden of side effects.
For antioxidant support, while there are many supplements available, NAC is unique in its direct role as a precursor to glutathione. This distinguishes it from other antioxidants that are either not as effective in boosting glutathione or do not have NAC’s additional benefits for respiratory and mental health. Lastly, NAC has been toted as an anti-cancer supplement and treatment due to it’s many benefits (inflammation, stress reduction, antioxidant boost) that directly, and indirectly, aid in cancer treatment.
What are Different Forms of NAC?
N-Acetylcysteine is available in various forms, allowing for versatility in administration and use. The most common form is oral supplements, which come in capsules or powders. These are widely used for general antioxidant support or as a dietary supplement. Effervescent tablets are another form, often used for respiratory conditions, as they can be dissolved in water to create a solution that is both easy to ingest and soothing for the throat. In medical settings, NAC is available in intravenous or inhalable forms, which are used in acute cases, such as treating an acetaminophen overdose or loosening mucus in the airways.
Each form of NAC has its specific use cases, with the method of administration being chosen based on the condition being treated, the required dosage, and patient preference. The oral form is suitable for most uses, while inhalable and intravenous forms are reserved for more severe conditions or when rapid delivery is necessary.
- Capsules
- Powders
- Tablets
- Intravenous and inhalable forms
How can NAC Be Administered?
N-Acetylcysteine administration depends on the form and intended use. When taken orally as a supplement, it can be consumed with or without food, although some people may find taking it with food can minimize gastrointestinal discomfort. Typically, NAC supplements are taken in divided doses throughout the day. Inhalable forms are administered with a nebulizer, providing direct delivery to the lungs, which is particularly effective for respiratory conditions. Intravenous administration is used in medical emergencies, providing the fastest delivery of NAC into the system.
Users should be mindful of timing when taking NAC. It’s often advised to avoid taking antioxidant supplements at the exact same time as exercising, as it may interfere with the body’s natural oxidative response to exercise, which plays a role in conditioning. Additionally, to maximize absorption, it may be best to avoid taking NAC alongside large amounts of protein. As always, users should consult healthcare providers for personalized advice on timing and combination with food or other supplements.
Can N-Acetylcysteine (NAC) Be Used as Treatment for Mental Health Disorders?
Yes, NAC can be used as a treatment for certain mental health disorders. Clinical studies have shown promising results in using NAC as an adjunct treatment for conditions like depression, bipolar disorder, and obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD). Studies also show NAC as being one of the best anxiety supplements as it helps regulate stress, one of the biggest causes of anxiety.
Its mechanism of modulating glutamate and dopamine in the brain suggests a neuroprotective role that can help manage psychiatric symptoms. However, it’s crucial to note that NAC should not replace conventional treatments but rather serve as a complementary approach under the guidance of a mental health professional.
Despite the potential benefits, further research is needed to establish standardized dosing and to fully understand the extent of NAC’s effectiveness for mental health disorders. Patients interested in NAC for mental health treatment should consult with their healthcare providers to consider the current evidence and determine if NAC is a suitable option for their individual health plan.
Is N-Acetylcysteine (NAC) Available Over-The-Counter?
Yes, N-Acetylcysteine is available over-the-counter (OTC) in many countries, including the United States. It is commonly found in health food stores, pharmacies, and online marketplaces as a dietary supplement. However, it’s important to note that the availability of NAC as an OTC supplement is subject to regulatory changes, and individuals should stay informed about the current status in their region. For example, the FDA has had discussions about the regulation of NAC as a supplement, given its status as an approved medication for certain conditions.
When purchasing NAC over-the-counter, consumers should look for reputable brands and be mindful of the concentration and purity of the product. It’s advisable to seek products that have undergone third-party testing for quality assurance. As with any supplement, it’s recommended to consult with a healthcare provider before starting NAC, particularly for individuals with pre-existing health conditions or those taking other medications.
Are There Any Contraindications with Other Medications when Using N-Acetylcysteine (NAC)?
Yes, there are potential contraindications when using N-Acetylcysteine with certain other medications. NAC may interact with nitroglycerin and isosorbide, medications used to treat angina, potentially causing severe headaches and hypotension. It may also affect the way the body processes certain drugs through the liver, either increasing or decreasing their effects. Individuals taking activated charcoal should be aware that it can decrease the effectiveness of NAC if taken simultaneously, due to adsorption of the drug.
Because of these potential interactions, it is critical for individuals to inform their healthcare providers about all medications and supplements they are currently taking before starting NAC. This ensures a comprehensive review of any possible adverse interactions and the establishment of a safe and effective treatment plan tailored to the individual’s unique health profile.
Can N-Acetylcysteine (NAC) Be Used as A Preventive Measure for Certain Health Issues?
Yes, N-Acetylcysteine may serve as a preventive measure for certain health issues, particularly those associated with oxidative stress and inflammation, due to its antioxidant properties. Regular use of NAC supplements may help protect against cellular damage, support immune function, and maintain optimal levels of glutathione in the body. It has been explored for its potential in preventing exacerbations in chronic bronchitis and reducing the incidence of contrast-induced nephropathy in patients undergoing radiographic procedures.
However, the role of NAC in prevention should be considered alongside other health strategies, such as a balanced diet and regular exercise. While NAC may contribute to a preventive health regimen, it is not a substitute for comprehensive lifestyle choices or medical interventions that have well-established preventive benefits. As always, decisions about using NAC for prevention should be made in consultation with a healthcare provider, taking into account an individual’s medical history and current health status.
What are Lifestyle Considerations when Incorporating NAC Into Your Wellness Routine?
Incorporating N-Acetylcysteine into one’s wellness routine requires consideration of various lifestyle factors to maximize its benefits. Consistency in supplementation is key, as the body’s glutathione levels are affected by ongoing metabolic processes. Individuals should also be aware of their overall nutrient intake, as a well-rounded diet supports the actions of NAC and the synthesis of glutathione. Lifestyle habits such as regular exercise, adequate hydration, and avoiding excessive alcohol consumption can complement the effects of NAC and promote overall well-being.
For those specifically using NAC for its respiratory benefits, incorporating breathing exercises and avoiding exposure to pollutants where possible can be beneficial. It’s also recommended to engage in regular medical check-ups, as healthcare providers can offer personalized advice and adjust NAC supplementation based on any changes in health status or medication regimens. Lifestyle adjustments should be approached holistically, with NAC being one component of a broader commitment to health.
Are There Any Dietary Sources Of N-Acetylcysteine (NAC) That Can Be Obtained Naturally?
No, N-Acetylcysteine (NAC) itself is not found in dietary sources. However, cysteine, the amino acid that NAC is derived from, is present in many high-protein foods. Individuals can increase their intake of cysteine by consuming meats, dairy products, and certain plant-based proteins such as lentils and sunflower seeds. The body can convert cysteine into glutathione, an antioxidant that plays a crucial role in protecting cells from oxidative stress and maintaining immune health. While direct dietary sources of NAC are not available, a diet rich in cysteine can support the body’s natural production of glutathione.
For those looking to boost their cysteine intake specifically for health benefits related to NAC, focusing on a balanced diet with sufficient protein is important. Some health professionals might suggest dietary supplements to ensure adequate levels of cysteine, especially for individuals with certain health conditions or dietary restrictions that limit protein intake. Before making any significant changes to one’s diet or starting supplements, it’s advisable to consult with a healthcare provider to ensure these adjustments align with personal health needs and goals.



