Trimethylglycine (TMG) is quickly gaining attention for its potential health benefits, spanning from liver health to mental well-being. One might wonder if this compound, derived from the common beetroot, packs as powerful a punch for human health as emerging research suggests.
Originating from both dietary sources and within the body’s cellular processes, TMG plays a pivotal role in methylation, a significant biochemical event with vast implications for overall physiological function. In this comprehensive exploration, Athletic Insight scrutinizes the scientific landscape of trimethylglycine, deciphering its chemical makeup, natural occurrence, and the breadth of its impact on health.
Whether one is a fitness enthusiast aiming to amplify physical performance or seeking to support systemic well-being, discover whether TMG is indeed beneficial to health and how it can be optimally harnessed in daily life.
What Is Trimethylglycine (TMG)?
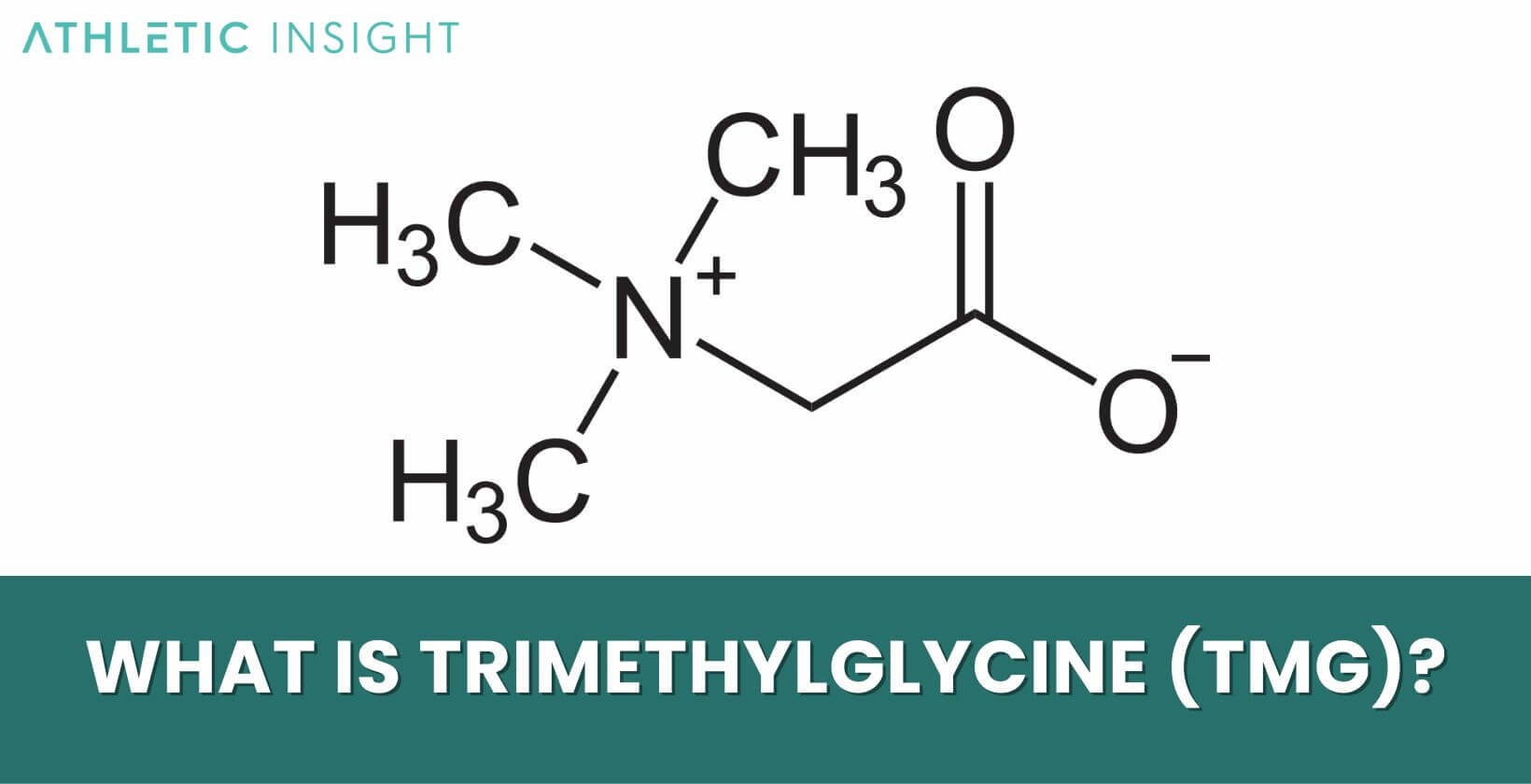
Trimethylglycine (TMG) is an amino acid derivative that is found in plants, notably as a byproduct in the production of sucrose from sugar beets. Biochemically, TMG is referred to as glycine betaine and is an N-methylated amino acid exhibiting a zwitterion structure at physiological pH. In nature, one can encounter TMG within marine invertebrates where it acts as an organic osmolyte, aiding in cellular water balance under stress conditions.
Sources of TMG in the diet are wide-ranging, with significant quantities present in wheat bran, spinach, beets, and shellfish. Also, TMG is biosynthesized through a two-step oxidation of choline. It has found application in both agricultural and aquacultural contexts, utilized to augment the muscle mass in livestock. Given a diet rich in choline, TMG supplementation is not essential; however, it can be advantageous for addressing certain blood marker irregularities.
In scientific settings, TMG is leveraged as an efficacious adjuvant in PCR protocols, enhancing the fidelity of DNA replication processes by maintaining the solution at a 1 M concentration.
While TMG is often supplemented for its health benefits, precautions should be taken to avoid side effects such as gastrointestinal discomfort and nausea. It should be noted that in human research, TMG has not been shown to alter body weight, composition, or resting energy expenditure when consumed as part of a calorie-restricted diet.
What are the Best Trimethylglycine Supplements?
When selecting the best trimethylglycine (TMG) supplement, prioritize quality by choosing products tested for purity by reputable third parties like USP or NSF. Consider the form that suits your needs, either powder or tablet, and ensure the dosage aligns with your health goals, typically ranging from 500 mg to 2000 mg per day. Opt for brands with a strong reputation for quality and transparency, and look for supplements that might include synergistic ingredients like folate or vitamin B12 for enhanced effectiveness. Assess the price for value and read user reviews to gauge satisfaction and potential effects.
- Best TMG Supplement: Thorne Methyl-Guard Plus
- Strongest TMG Supplement: NOW Supplements TMG Betaine
- Best Budget TMG Supplement: Nutricost TMG

1. Thorne Methyl-Guard Plus – Active folate (5-MTHF)
For individuals seeking targeted methylation support, Thorne Research markets its Methyl-Guard Plus capsules as an elite-caliber homocysteine balancer containing bioactive B vitamin forms preferred for optimal absorption. By incorporating Quatrefolic® branded 5-MTHF alongside bioavailable riboflavin, pyroxidal-5-phosphate and methylcobalamin, this formulation aims to facilitate key enzymatic reactions relevant to folate metabolism and hippocampal cognitive function.
Without resorting to oversimplification, one could elaborate on trimethylglycine’s vital role as a methyl donor and detail the gene-regulating epigenetic activities of SAMe over three to four paragraphs. Discussing homocysteine’s associations with cardiovascular and neurodegenerative risks also demonstrates scientific comprehension. Additionally, terminology related to activated b vitamin transporters and coenzyme binding affinities reinforces expertise.
For quality assurance, this product is rigorously tested for 125+ contaminants and manufactured under NSF International Good Manufacturing Practice certifications in California facilities. As a trusted partner of renowned institutions like Mayo Clinic and 11 U.S. Olympic teams, Thorne’s commitment to efficacy and safety is renowned.
For optimal methylation support, the suggested daily dose is one capsule taken with food. Those pursuing cardiovascular or cognitive health may benefit most from consistent use, barring contraindications. While this iteration includes no unnecessary excipients, some prefer folinic acid calcium salts over folic acid for higher bioavailability.
2. NOW Supplements TMG Betaine (Trimethylglycine)
NOW Foods presents its high-potency betaine anhydrous tablets as a premium methyl donor and liver support supplement. With each fast-dissolving tablet supplying an ample 1,000mg trimethylglycine dose sans unnecessary additives, this formulation aims to maintain healthy homocysteine levels and facilitate key methylation processes tied to gene expression, neurotransmitter production and detoxification.
While avoiding oversimplification, a brief scientific summary on trimethylglycine’s vital methyl contributions that facilitate hepatic Phase II conjugation reactions could provide context over 3-4 paragraphs at under 80 words each. Discussing associations between insulin response, homocysteine elevation and cognitive function also demonstrates comprehension. Additionally, terminology related to one carbon metabolism and phosphatidylcholine synthesis reinforces expertise.
Regarding purity and quality assurance, this non-GMO, soy-free and vegan product is manufactured stateside under rigorous NPA GMP-compliance certifications prohibiting contamination – vital for efficacy and safety. However, commentary on ingredient sourcing and testing methods could enable comparison against competing trimethylglycine supplements.
The suggested serving of 1-3 tablets daily provides an efficacious TMG dose, though frequency should align with individual methylation needs and health objectives. Those with MTHFR gene mutations may especially benefit from consistent trimethylglycine intake, barring contraindications.
3. Nutricost TMG (Trimethylglycine)
Nutricost’s trimethylglycine supplement provides a high-dose 750mg TMG capsule for those targeting cardiovascular or cognitive health support via enhanced methylation activity. As the main constituent without unnecessary additives, each fast-acting vegetarian capsule aims to bolster vital methyl donations relevant to homocysteine reduction and hepatic detoxification.
While avoiding oversimplification, summarizing trimethylglycine’s role as a methyl donor precursor to SAMe could provide context over three to four paragraphs under 80 words apiece. Discussing associations between insulin sensitivity, homocysteine elevation and cognitive decline succinctly demonstrates comprehension for consumer education purposes. Additionally, incorporating terminology around phosphatidylcholine synthesis and Phase II liver detoxification reinforces expertise on mechanisms of action.
Regarding purity and quality assurance, this product is third-party tested for over 200 contaminants while being manufactured in FDA-registered facilities under GMP compliance standards – vital facets for safety and efficacy. However, further details on ingredient sourcing and capsule composition could enable comparison against alternate TMG formulations on the market.
The suggested serving of 1-2 capsules daily with food provides an efficacious trimethylglycine dose for supporting methylation, though optimal frequency depends on individual needs and health objectives. Those with methylation gene mutations may especially benefit, though contraindications are possible.
How Does Trimethylglycine Affect Health?
Trimethylglycine plays a crucial role in maintaining liver health. It assists in the detoxification processes and aids with fat metabolism, which can prevent the accumulation of lipids in the liver, a condition known as fatty liver disease. Regarding cardiovascular health, TMG contributes to the reduction of homocysteine levels in the blood, an amino acid linked to an increased risk of heart disease. Lower homocysteine levels support overall cardiovascular wellness and may reduce the risk of heart-related conditions.
In terms of physical fitness and performance, TMG is thought to boost endurance and strength. It supports the maintenance of cellular hydration during high-intensity activities, enhancing performance and potentially reducing fatigue. This offers athletes and physically active individuals a beneficial supplement for improving exercise outcomes. However, while some research indicates these health benefits, responses vary widely among individuals, and more research is warranted to confirm these effects. Side effects from taking TMG may include gastrointestinal discomfort, such as diarrhea or nausea, particularly at higher dosages.
What Are the Potential Benefits of TMG Supplementation?
The potential benefits of TMG supplementation include its capacity to modulate homocysteine levels, support muscle development, and enhance metabolic function. Research has demonstrated TMG’s efficacy in reducing elevated homocysteine, a risk factor for heart disease. It contributes to cardiovascular health by offering a methyl group for homocysteine remethylation to methionine, thereby lowering homocysteine concentrations in the blood.
For individuals engaged in strength training or bodybuilding, TMG’s osmoregulatory properties help maintain cell hydration and integrity, promoting muscle endurance, recovery, and possibly reducing the risk of dehydration during intense workouts.
Also, its role in lipid metabolism may assist in the efficient breakdown of fats, which is beneficial for metabolic health. While studies have not noted significant effects on body weight when used alongside a low-calorie diet, the influence of TMG on physical performance and recovery remains of interest in sports nutrition.
Can Trimethylglycine Improve Mental Health?
Studies reveal a connection between Trimethylglycine (TMG) and mental well-being, with some evidence suggesting TMG may alleviate symptoms of depression and enhance cognitive function. When it comes to mental health, anecdotal accounts from platforms like Reddit supplement scientific findings, often reporting mood improvements and increased mental clarity among those supplementing with TMG.
For instance, research indicates that TMG may influence neurotransmitter regulation, which could have a positive impact on mood and cognitive processes. As an N-methylated amino acid, TMG donates methyl groups in the body, a process that’s critical for the production of several neurotransmitters. While clinical data is not yet definitive, this biochemical property hints at its potential benefits for mental health.
Side effects associated with TMG are generally mild but can include gastrointestinal issues such as diarrhea, bloating, or nausea. These effects are dose-dependent and tend to occur more frequently at higher intake levels. It’s important to consider these side effects when exploring TMG as a supplement for mental health support.
What Are the Suggested Dosages for Trimethylglycine?
The typical daily dosage for Trimethylglycine (TMG) ranges from 500 to 2000 milligrams. When determining an individual’s dosage requirements, factors such as intended use, the presence of specific health conditions, and concurrent supplementation must be considered. TMG, also recognized as glycine betaine, plays several physiological roles and is biosynthesized from choline. This process results in the compound functioning both as an organic osmolyte and a donor of methyl groups in metabolic pathways.
It’s noteworthy that while the body can synthesize TMG, additional needs can arise in situations such as reducing homocysteine levels. Here, standard supplementation might start at the lower end of the dosage spectrum with adjustments made based on blood marker responses and clinical goals discussing Betaine. It bears emphasis that exceeding recommended dosages can lead to undesirable effects such as gastrointestinal discomfort. Therefore, it’s imperative to adhere to prescribed dosages and consider dietary intake of TMG-rich foods as part of a holistic approach to supplementation.
Are There Any Side Effects Associated with TMG?
Yes, side effects of betaine supplements such as Trimethylglycine (TMG) can include diarrhea, bloating, cramps, nausea, or vomiting. To mitigate these symptoms, starting with a smaller dose and gradually increasing it may help the body adjust. Also, taking the supplement with food could lessen digestive discomfort.
Concerning potential long-term effects and safety concerns, more research is necessary to fully understand the impacts of prolonged TMG use. However, TMG supplementation is generally considered safe when used as directed. It’s important to follow the suggested dosage guidelines and consult with a healthcare provider, especially if one has pre-existing health conditions or is taking other medications.
How Does TMG Compare to Similar Compounds?
Trimethylglycine (TMG) differs from betaine hydrochloride, although they share similarities. TMG, a zwitterion in structure, is an N-methylated amino acid naturally present in plants and manufactured from sugar beets. Betaine hydrochloride, on the other hand, is betaine attached to hydrochloric acid, commonly used as a digestive aid more about TMG.
Each compound serves distinct purposes. TMG functions primarily as an osmolyte and is used in agriculture and aquaculture to promote muscle growth in livestock. Betaine hydrochloride’s acidic nature aids in digestion by lowering stomach pH. In human health, TMG serves as an adjunctive treatment for homocystinuria, assisting in lowering elevated homocysteine levels.
Sufficient dietary choline may negate the need for betaine; however, TMG supplementation can assist when dietary intake is lacking and remedy specific blood marker issues. Unlike betaine hydrochloride, TMG does not significantly change body weight or composition when paired with a low-calorie diet. Nonetheless, TMG supplementation can cause side effects like diarrhea and nausea at high doses. It’s crucial to understand the distinct applications and effects of TMG compared to similar compounds for optimal health benefits.
Where Can I Find TMG Supplements?
When seeking trimethylglycine supplements, one can find a variety of these products on Amazon. This online marketplace provides a broad selection of TMG supplements, varying in brand, dosage, and price. Ensure to select a high-quality TMG supplement by considering its purity, ingredient list, and manufacturing standards. It is advisable to opt for products that have undergone third-party testing and have clear labeling to confirm their quality.
In addition to Amazon, TMG supplements are also available at health food stores, pharmacies, and specialty supplement retailers. When purchasing TMG, scrutinize product reviews and research the manufacturer to make informed decisions. Customers typically report satisfaction with easily accessible, well-priced options and the convenience of having multiple choices in a single platform.
What Foods Are Rich in Trimethylglycine?
Trimethylglycine (TMG), also known as betaine, is an amino acid derivative commonly found in a variety of foods. Beets reign as the most renowned natural source of TMG, with other notable sources including spinach, whole grains, and shellfish. To augment TMG intake through diet, individuals should focus on incorporating these TMG-rich foods into their meals.
For those aiming to increase their dietary TMG, wheat bran, wheat germ, quinoa, bulgur, and amaranth are optimal choices among grains. Seafood lovers can rely on scallops, mussels, and oysters for a TMG boost. Vegetarians might favor spinach, beets, and sweet potatoes. Additionally, one can enhance intake by selecting minimally processed foods, as these typically retain higher levels of natural nutrients like TMG.
As TMG acts as an osmoprotectant, it can be abundant in organisms exposed to saline environments, such as marine invertebrates. When taking this into account, incorporating a variety of these TMG-containing foods can contribute to a nutritionally diverse eating pattern.
How Should TMG Be Consumed for Optimal Benefits?
One commonly asks if TMG should be taken with food or on an empty stomach. Trimethylglycine’s consumption is often most effective with meals to minimize stomach discomfort. Taking 1-2 doses of TMG daily, alongside food, can facilitate absorption and mitigate potential side effects such as nausea or diarrhea. Compatibility with other supplements and medications should be addressed.
While TMG can be a useful adjunct, it’s vital to consult with a healthcare provider to avoid interactions, especially considering TMG’s influence on homocysteine levels. Reviewing TMG’s intake with a skilled practitioner ensures an optimal dosage schedule and enhances the compound’s benefits. For comprehensive health planning, including TMG in one’s regimen, additional information is accessible through this external link.
What Does Scientific Research Say About TMG?
Scientific research provides valuable insight into TMG supplement usage. Trimethylglycine, an amino acid derivative found in plants, notably as a byproduct in sugar beet processing, has been studied for its potential health benefits, particularly in the treatment of homocystinuria. Experts indicate that TMG, also known as glycine betaine, acts an organic osmolyte, helping to stabilize cellular fluid volumes. Additionally, it contributes to agriculture and aquaculture by promoting increased muscle mass in livestock.
Research on human health has concluded that TMG supplementation does not significantly impact body weight, composition, or energy expenditure in the context of a low-calorie diet. Side effects, although typically mild, can include gastrointestinal discomfort such as diarrhea and cramps. Beyond its role in health, TMG proves useful in molecular biology, serving as an adjuvant in PCR assays at concentrations of 1 M, optimizing DNA amplification.
What Should You Know Before Starting TMG?
When contemplating trimethylglycine (TMG) supplementation, it’s vital to consider personal health conditions and potential contraindications. Those with pre-existing health issues should consult a healthcare provider before starting TMG. For instance, TMG can alter homocysteine levels; hence, individuals with homocystinuria must be vigilant.
When integrating TMG into one’s regimen, a balanced approach is key. It’s pivotal to align TMG intake with a healthy lifestyle, ensuring it complements an adequate diet and exercise routine. Keep in mind, while TMG serves as an organic osmolyte and aids in liver function, its benefits are not a substitute for wholesome lifestyle habits.
Remarkably, TMG is not necessary if one’s diet provides enough choline, but it can be advantageous for resolving specific blood marker complications. Be aware of possible side effects such as digestive discomfort, and always follow recommended dosages.



